In this article I will explain with an example, how to use SqlCommand ExecuteNonQuery in C# and VB.Net while developing ASP.Net, Windows and Console applications.
Database
I have made use of the following table Customers with the schema as follows.
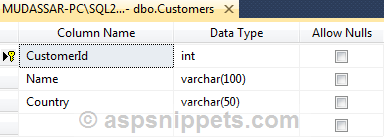
Note: You can download the database table SQL by clicking the download link below.
The ExecuteNonQuery method
ExecuteNonQuery is basically used for operations where there is nothing returned from the SQL Query or
Stored Procedure. Preferred use will be for INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE Operations.
Namespaces
You will need to import the following namespaces.
C#
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Configuration;
VB.Net
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Data.SqlClient
Imports System.Configuration
INSERT
Initially, the connection is read from App.Config or Web.Config file and object of SqlConnection class is created using it.
Then, an object of SqlCommand class is created and the insert query is executed.
The values of the name and country are added as parameter to SqlCommand object.
Finally, the connection is opened and the ExecuteNonQuery function is executed.
C#
protected void Page_Load(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
string name = "Mudassar Khan";
string country = "India";
string sql = "INSERT INTO Customers (Name, Country) VALUES (@Name, @Country)";
string constr = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["constr"].ConnectionString;
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(constr))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, con))
{
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", name);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Country", country);
con.Open();
int rowsAffected = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
}
}
VB.Net
Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)Handles Me.Load
Dim name As String = "Mudassar Khan"
Dim country As String = "India"
Dim sql As String = "INSERT INTO Customers (Name, Country) VALUES (@Name, @Country)"
Dim constr As String = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings("constr").ConnectionString
Using con As SqlConnection = New SqlConnection(constr)
Using cmd As SqlCommand = New SqlCommand(sql, con)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", name)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Country", country)
con.Open()
Dim rowsAffected As Integer = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
con.Close()
End Using
End Using
End Sub
The screenshot below displays the rows affected.

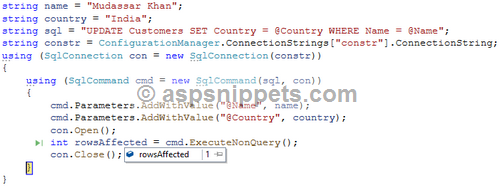
UPDATE
Initially, the connection is read from App.Config or Web.Config file and object of SqlConnection class is created using it.
Then, an object of SqlCommand class is created and the update query is executed.
The values of the name and country are added as parameter to SqlCommand object.
Finally, the connection is opened and the ExecuteNonQuery function is executed.
C#
protected void Page_Load(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
string name = "Mudassar Khan";
string country = "India";
string sql = "UPDATE Customers SET Country = @Country WHERE Name = @Name";
string constr = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["constr"].ConnectionString;
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(constr))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, con))
{
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", name);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Country", country);
con.Open();
int rowsAffected = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
}
}
VB.Net
Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)Handles Me.Load
Dim name As String = "Mudassar Khan"
Dim country As String = "India"
Dim sql As String = "UPDATE Customers SET Country = @Country WHERE Name = @Name"
Dim constr As String = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings("constr").ConnectionString
Using con As SqlConnection = New SqlConnection(constr)
Using cmd As SqlCommand = New SqlCommand(sql, con)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", name)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Country", country)
con.Open()
Dim rowsAffected As Integer = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
con.Close()
End Using
End Using
End Sub
The screenshot below displays the rows affected.
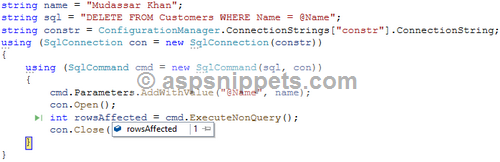
DELETE
Initially, the connection string is fetched from the App.Config file and a object of SqlConnection class is created using it.
Then, an object of SqlCommand class is created and the DELETE query is passed to it as parameter.
The values of the name and country are added as parameter to SqlCommand object.
Finally, the connection is opened and the ExecuteNonQuery function is executed.
C#
protected void Page_Load(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
string name = "Mudassar Khan";
string sql = "DELETE FROM Customers WHERE Name = @Name";
string constr = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["constr"].ConnectionString;
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(constr))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, con))
{
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", name);
con.Open();
int rowsAffected = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
}
}
VB.Net
Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)Handles Me.Load
Dim name As String = "Mudassar Khan"
Dim sql As String = "DELETE FROM Customers WHERE Name = @Name"
Dim constr As String = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings("constr").ConnectionString
Using con As SqlConnection = New SqlConnection(constr)
Using cmd As SqlCommand = New SqlCommand(sql, con)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", name)
con.Open()
Dim rowsAffected As Integer = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
con.Close()
End Using
End Using
End Sub
The screenshot below displays the rows affected.
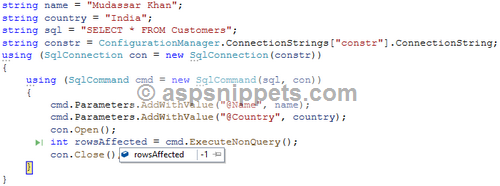
What happens when I use ExecuteNonQuery for SELECT statement?
ExecuteNonQuery will work flawlessly for SELECT SQL Query or
Stored Procedure but that will simply execute the query and do nothing. Even if you use it, you will not throw any error but the Rows Affected will be negative i.e. -1.
C#
protected void Page_Load(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
string name = "Mudassar Khan";
string country = "India";
string sql = "SELECT * FROM Customers";
string constr = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["constr"].ConnectionString;
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(constr))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, con))
{
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", name);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Country", country);
con.Open();
int rowsAffected = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
}
}
VB.Net
Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)Handles Me.Load
Dim name As String = "Mudassar Khan"
Dim country As String = "India"
Dim sql As String = "SELECT * FROM Customers"
Dim constr As String = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings("constr").ConnectionString
Using con As SqlConnection = New SqlConnection(constr)
Using cmd As SqlCommand = New SqlCommand(sql, con)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", name)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Country", country)
con.Open()
Dim rowsAffected As Integer = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
con.Close()
End Using
End Using
End Sub
The screenshot below displays the rows affected returned -1.
Thus, concluding it, we must use ExecuteNonQuery for INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE operations only.